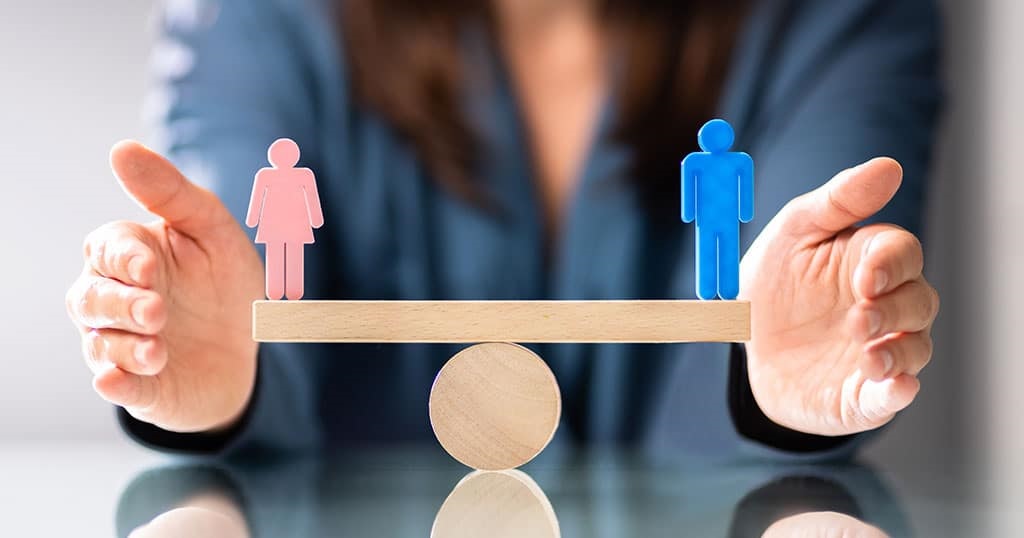
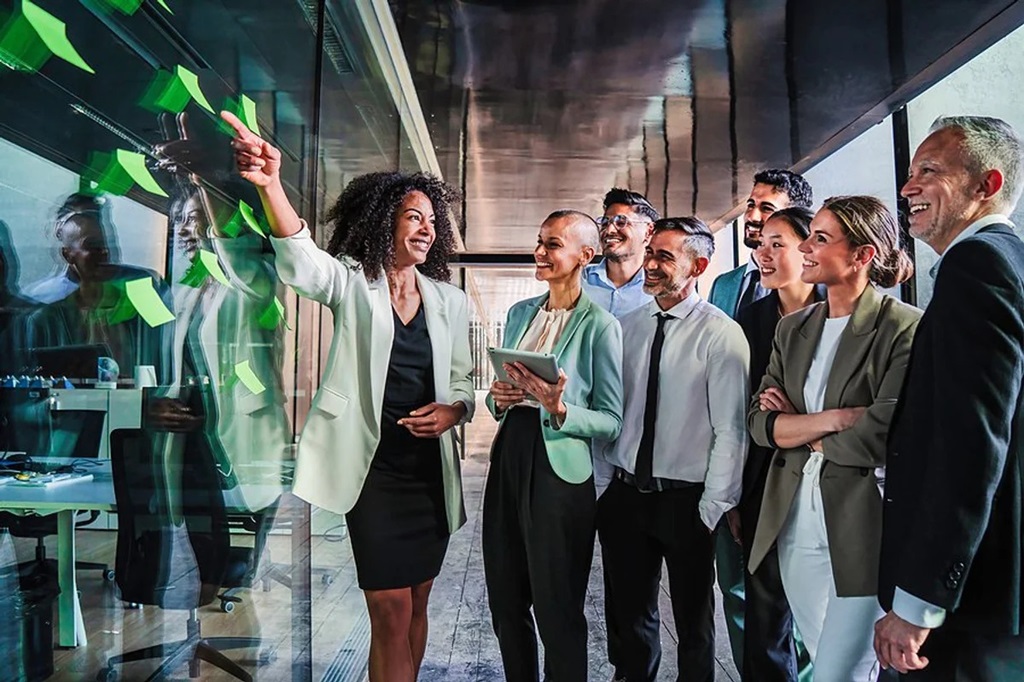
In today’s rapidly evolving world, promoting gender equality in the workplace is not just a moral imperative but also a strategic business decision. Companies that embrace diversity and inclusion experience a myriad of benefits, from improved workplace culture to increased creativity and innovation. In this article, we will explore how to promote gender equality in the workplace and create a more inclusive work environment.
I. Understanding The Gender Equality in The Workplace
A. Definition of gender equality in the workplace
Gender equality in the workplace refers to the equal rights, opportunities, and treatment of all employees, regardless of their gender identity. It involves creating an environment where individuals are judged based on their skills, abilities, and contributions rather than stereotypes or biases.
B. Importance of promoting gender equality
The significance of promoting gender equality cannot be overstated. It not only aligns with principles of fairness and justice but also contributes to a more vibrant and dynamic workplace.
C. Current state of gender equality in workplaces
While progress has been made, there is still work to be done. Gender stereotypes, biases, and the gender pay gap persist, creating obstacles for many individuals in their professional lives.
II. Benefits of Gender Equality
A. Improved workplace culture
A diverse and inclusive workplace culture fosters a sense of belonging and acceptance among employees. This, in turn, leads to higher levels of collaboration and teamwork.
B. Increased creativity and innovation
Diverse teams bring a variety of perspectives and ideas, driving innovation and problem-solving. Companies that prioritize gender equality are more likely to outperform their competitors in the long run.
C. Enhanced employee satisfaction and retention
Employees are more likely to stay with a company that values and supports them. Gender equality initiatives contribute to higher job satisfaction and, consequently, lower turnover rates.
III. Barriers to Gender Equality

A. Gender stereotypes and biases
Societal expectations and stereotypes often influence how individuals are perceived in the workplace. Overcoming these biases is crucial for achieving true gender equality.
B. Lack of equal opportunities
Unequal access to opportunities hinders career progression for many individuals. Companies must actively strive to provide equal opportunities for professional growth.
C. Gender pay gap
The persistent gender pay gap is a stark reminder of inequality. Addressing this issue requires a comprehensive approach, including transparent salary structures and fair evaluation processes.
IV. Strategies for Promoting Gender Equality
A. Implementing inclusive hiring practices
Ensure that recruitment processes are free from biases and promote diversity from the outset. This includes using inclusive language in job descriptions and actively seeking a diverse pool of candidates.
B. Providing equal opportunities for professional development
Create programs that support the professional growth of all employees, regardless of gender. This may involve mentorship programs, training initiatives, and leadership development opportunities.
C. Addressing the gender pay gap
Regularly review and adjust salary structures to eliminate gender disparities. Transparent communication about pay scales can also contribute to a more equitable workplace.
D. Encouraging work-life balance for all employees
Promote policies that support work-life balance, such as flexible working hours and remote work options. This benefits all employees, irrespective of gender.
V. Creating Inclusive Policies
A. Developing and enforcing anti-discrimination policies
Clearly define and communicate policies that prohibit discrimination based on gender or any other characteristic. Ensure that employees are aware of their rights and how to report any discriminatory behavior.
B. Establishing flexible work arrangements
Recognize that employees have diverse needs and responsibilities. Implement flexible work arrangements, such as part-time schedules or compressed workweeks, to accommodate various lifestyles.
C. Providing parental leave for all genders
Offer parental leave policies that are inclusive and supportive of all genders. This helps break down traditional gender roles and promotes a more equal division of caregiving responsibilities.
VI. Education and Training

A. Conducting diversity and inclusion training
Mandatory training sessions can raise awareness about unconscious biases and promote a more inclusive workplace culture. Ensure that all employees, from entry-level to leadership, participate.
B. Raising awareness about unconscious biases
Regularly communicate about unconscious biases and how they can impact decision-making. Encourage self-reflection and open discussions to challenge and overcome biases.
C. Empowering employees to be allies
Promote the concept of allyship within the organization. Encourage employees to support and advocate for their colleagues, fostering a culture of mutual respect and understanding.
VII. Leading by Example
A. Promoting gender diversity in leadership roles
Actively work towards increasing the representation of women and other underrepresented genders in leadership positions. Leadership should reflect the diversity of the workforce.
B. Showcasing success stories of gender equality in the workplace
Highlighting successful examples within the organization can inspire others and demonstrate the positive impact of gender equality initiatives.
VIII. Measuring and Monitoring Progress
A. Implementing gender diversity metrics
Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) related to gender diversity and regularly assess progress. Use data to identify areas for improvement and celebrate achievements.
B. Regularly reviewing and adjusting policies
A commitment to continuous improvement involves regularly evaluating existing policies and making adjustments as needed. This ensures that gender equality initiatives remain effective over time.
C. Encouraging open communication and feedback
Create channels for employees to provide feedback on gender equality initiatives. This fosters a sense of transparency and involvement in the process.
IX. Overcoming Resistance

A. Addressing common misconceptions about gender equality
Acknowledge and address common myths and misconceptions about gender equality. Providing accurate information can help dispel resistance.
B. Engaging in open dialogue with resistant individuals
Encourage open conversations with individuals who may be resistant to change. Understanding their concerns and perspectives is crucial for fostering a more inclusive environment.
X. The Role of Men in Promoting Gender Equality
A. Breaking down stereotypes about masculinity
Challenge traditional notions of masculinity that may contribute to gender inequality. Encourage men to embrace a more inclusive and supportive definition of masculinity.
B. Becoming allies in the workplace
Men can play a crucial role in advocating for gender equality. This involves actively supporting and amplifying the voices of women and other underrepresented genders.
C. Fostering a supportive environment for all employees
Create an inclusive culture where all employees feel valued and supported, regardless of their gender. This involves promoting a sense of belonging and camaraderie.
XI. Case Studies
A. Highlighting successful examples of gender equality initiatives
Share real-life examples of companies that have successfully implemented gender equality initiatives. Discuss the specific strategies they employed and the positive outcomes achieved.
B. Discussing lessons learned and best practices
Explore lessons learned from case studies and distill best practices that can be applied in various organizational contexts.
XII. The Future of Gender Equality in the Workplace

A. Emerging trends and opportunities
Examine emerging trends in the field of gender equality and how they may shape the future of workplaces. This may include the use of technology and innovative policies.
B. The role of technology in promoting gender equality
Explore how technology can be leveraged to advance gender equality, from AI-driven hiring processes to virtual mentorship programs.
XIII. Conclusion
A. Summarizing key points
In conclusion, promoting gender equality in the workplace is a multifaceted endeavor that requires commitment and action from all levels of an organization. The benefits are not only moral but also strategic, contributing to a more innovative, inclusive, and successful workplace.
B. Reinforcing the importance of ongoing efforts for gender equality
While progress has been made, there is still work to be done. Organizations must remain vigilant and proactive in their efforts to promote gender equality.
FAQs
Q: Why is gender equality important in the workplace?
A: Gender equality fosters a more inclusive and innovative workplace, contributing to improved workplace culture, increased creativity, and enhanced employee satisfaction.
Q: How can companies address the gender pay gap?
A: Companies can address the gender pay gap by regularly reviewing salary structures, ensuring transparency in pay scales, and promoting equal opportunities for professional development.
Q: What role can men play in promoting gender equality?
A: Men can play a crucial role by challenging stereotypes, becoming allies, and fostering a supportive environment that values and includes all employees.
Q: How can organizations measure progress in gender equality initiatives?
A: Organizations can measure progress by implementing gender diversity metrics, regularly reviewing policies, and encouraging open communication and feedback from employees.
Q: What are some emerging trends in promoting gender equality in the workplace?
A: Emerging trends include leveraging technology for inclusive hiring processes, implementing virtual mentorship programs, and exploring innovative policies to advance gender equality.